In a Living Cell Which Process Uses Up Atp
This transfer is carried out by special enzymes that couple the release of energy from ATP to cellular activities that require energy. ATP in Living Systems.
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists
Microorganisms capture and store energy metabolized from food and light sources in the form of ATP.

. ATP is the most widely distributed high-energy compound within the human body Ritter 1996 p. Adenosine triphosphate ATP is an organic compound and hydrotrope that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells such as muscle contraction nerve impulse propagation condensate dissolution and chemical synthesis. All living things use ATP.
It is the main energy currency of the cell and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light cellular respiration and fermentation. Photosynthesis in cells is another type of metabolic pathway that organisms use to make sugar. Plant cells use ATP for respiration photosynthesis making cell walls Direct active transport takes place in cells of organisms this is when ATP breaks.
Substrate phosphorylation is a type of metabolic reaction that makes ATP by the physical addition of a phosphate group to ADP. Processes Which Require Energy. In a living cell which process uses up atp.
Make for growth and repair. Adenosine triphosphate ATP is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The cells energy yielding reactions synthesise ATP and ATP is used by the cell in all forms of work.
Cellular respiration is a type of metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to make adenosine triphosphate or ATP. The body is a complex organism and as such it takes energy to maintain proper functioning. CThey act as coenzymes so that fats can be synthesizedDThey are an integral part of the cell membrane important in.
Found in all known forms of life ATP is often referred to as the molecular unit of currency of intracellular energy transfer. It is present in all living organisms and is used to fuel within a cell. The high energy bond is broken and a phosphoryl group is removed.
What are 6 ways ATP is used. Chemistry 21062019 2030 flowergirly34. What are 6 ways ATP is used.
Adenosine triphosphate is the immediate source of energy in an organism. Furthermore they confirm that budding yeast growing on fermentable carbon sources primarily rely on glycolysis to produce ATP whereas non-fermentable carbon sources are metabolised. Adenosine Triphosphate ATP is the primary energy carrier in all living organisms on earth.
As ATP is used for energy a phosphate group or two are detached and either ADP or AMP is. Animals and plants are both able to convert ADP into ATP to generate energy. Motion Contraction Ion Transport.
Modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal Chemiosmosis a process of ATP production in cellular metabolism is used to generate 90 percent of the ATP made during glucose catabolism and is also the method used in the light reactions of photosynthesis to harness the energy of sunlight. The ATPalong with NADP is then used to provide energy for the carbohydrate synthesis also known as Calvi-Benson-Bassham-Cycle to make bonds between Carbon Hydrogen and Oxygen atoms which in turn come from carbon di-oxide and water present in. Adenosine triphosphate also known as ATP is a molecule that carries energy within cells.
If stock on hand is 250mgcapsule how many capsules should be given. What is the function of ATP molecules in living cellsAThey form a genetic material. What is ATP used for in an organism.
ATP is a complex nanomachine that serves as the primary energy currency of the cell Trefil 1992 p93. Animal cells use ATP in many different ways such as synthesis of new cells synthesis of amino acids active transport and for respiration. The cells energy yielding reactions synthesise ATP and ATP is used by the cell in all forms of work.
When the cell requires energy ATP is broken down through hydrolysis. Breakdown of glucose in cytoplasm. It allows the cell to store energy briefly and transport it within the cell to support endergonic chemical reactions.
ATP is able to power cellular processes by transferring a phosphate group to another molecule a process called phosphorylation. This reaction is commonly referred to as the hydrolysis of ATP. As you watch fill in the blanks below.
You are to give ampicillin with a recommended dose of 25mgkg to a child with a mass of 29kg. ATP adenosine phosphate groups activities Energy Needs of Cells Cells use ATP to. The full name of ATP is adenosine triphosphate.
It allows the cell to briefly store energy and transport it within the cell to. ATP synthesis utilizes energy obtained from multiple catabolic mechanisms including cellular respiration beta-oxidation and ketosis. Other questions on the subject.
Some plants cells that contain chlorophyll will use photosynthesis to make this reaction. Label the ATP diagram with what each shape represents. BThey hold energy from the oxidation of fuels in their high-energy phosphate bonds and the energy is used in various cell processes.
ATP Photosynthesis Cell Respiration WebQuest Task oneIntroduction to ATP Use the link to watch the What is ATP How is Works video. ATP functions as the energy currency for the cells. They first demonstrate that the QUEEN sensor detects the change in ATP levels seen upon glucose depletion and 2-deoxy-D-glucose-mediated inhibition of glycolysis.
ATP functions as the energy currency for cells. Since the basic reaction involves a water molecule ATP H 2 O ADP P i. Up chemical reactions.
Synthesis of complex molecules. ATP is a molecule in the cell that allows for quick and. A nanomachine is a complex precision microscopic-sized machine that fits the standard definition of a machine.
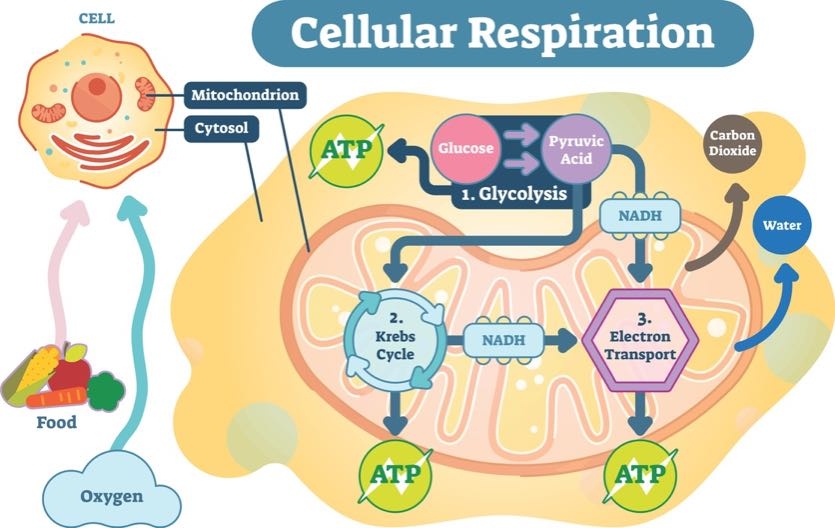
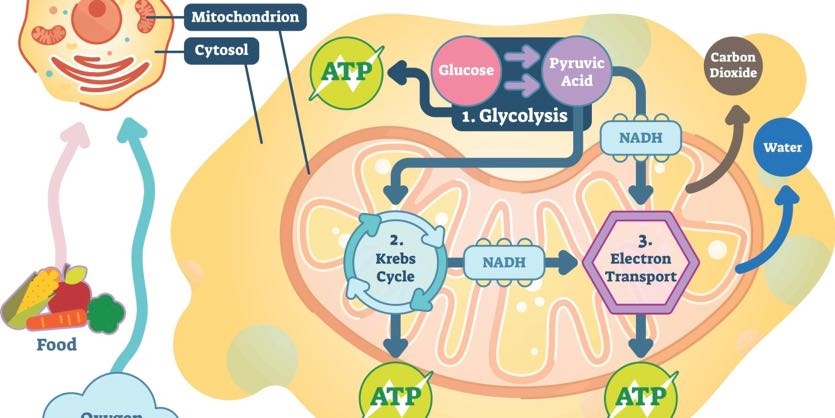
The structure of ATP is that of an RNA nucleotide with three phosphates attached. Adenosine triphosphate ATP is the energy currency of life and it provides that energy for most biological processes by being converted to ADP adenosine diphosphate. The main reactants are glucose and oxygen while the main products are carbon dioxide water and ATP.
Understanding Atp 10 Cellular Energy Questions Answered Ask The Scientists

Cellular Aerobic Energy Production Also Known As Cellular Respiration Aerobic Oxidation And Oxidative Phosphorylation Cellular Respiration Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Oxidative Phosphorylation

Aerobic Respiration Is A Biological Process That Takes Energy From Glucose And Other Cellular Respiration Biochemistry Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration
No comments for "In a Living Cell Which Process Uses Up Atp"
Post a Comment